Diabetic health issues are long-term conditions that impact millions globally. It affects the body’s ability to regulate blood sugar (glucose) levels, potentially leading to complications that influence overall health. However, medical advancements, lifestyle changes, and effective management strategies have greatly enhanced the quality of life for individuals with diabetes.
Common Health Issues in Diabetics
1. High Blood Sugar (Hyperglycemia)
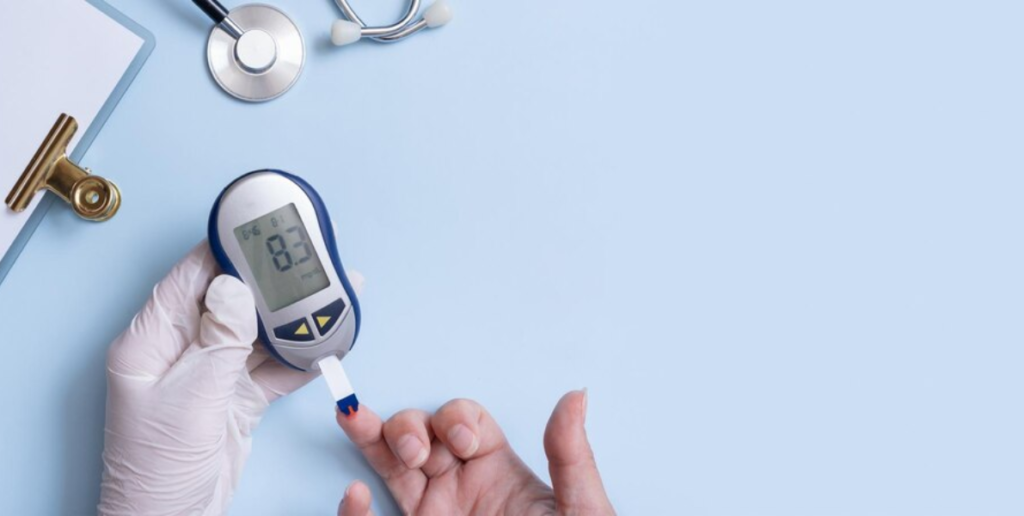
Hyperglycaemia occurs when blood sugar levels exceed normal ranges, leading to symptoms like excessive thirst, frequent urination, fatigue, and blurred vision. If not controlled, it can result in complications such as nerve damage, kidney disease, and cardiovascular issues.
2. Low Blood Sugar (Hypoglycaemia)
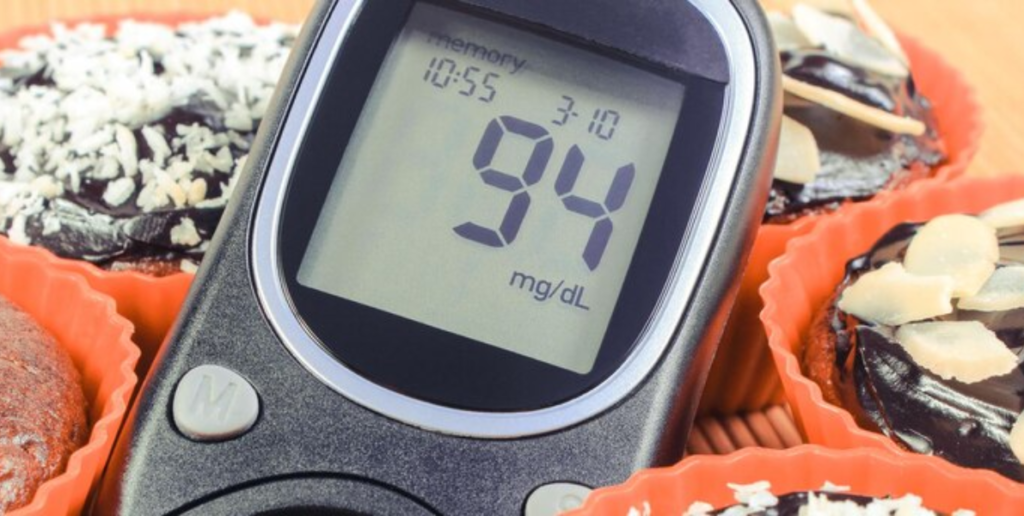

Hypoglycaemia happens when blood sugar levels drop too low, causing dizziness, confusion, shakiness, and, in severe cases, unconsciousness. It often results from missed meals, excessive physical activity, or an overdose of insulin or diabetes medication.
3. Nephropathy (Nerve Damage)

Diabetic nephropathy affects nerve function, causing numbness, tingling, or pain in the hands and feet. If not managed properly, it can lead to ulcers, infections, and, in extreme cases, amputation.
4. Cardiovascular Diseases
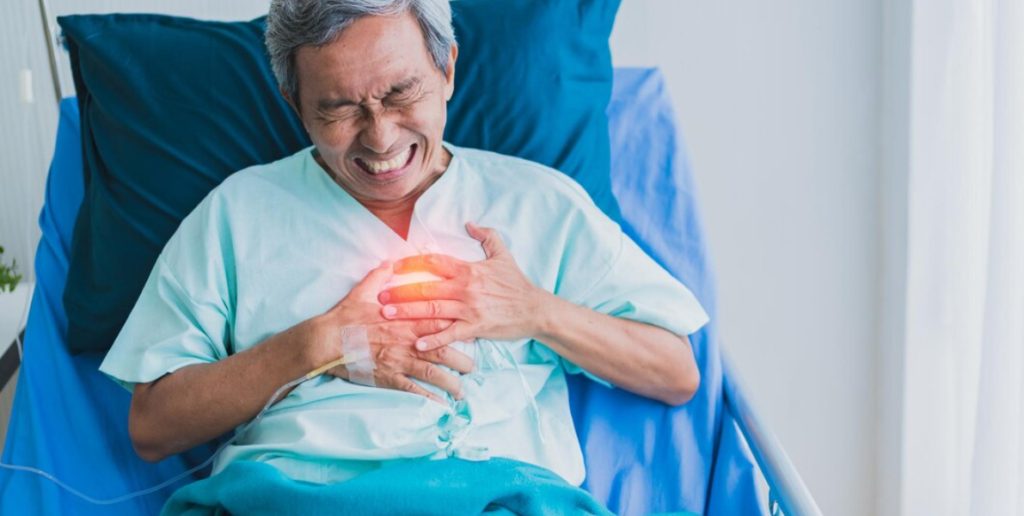

Diabetes increases the risk of heart disease and stroke as high blood sugar levels damage blood vessels. Individuals with diabetes are more prone to high blood pressure and cholesterol problems, further elevating cardiovascular risks.
5. Kidney Disease (Diabetic Nephropathy)
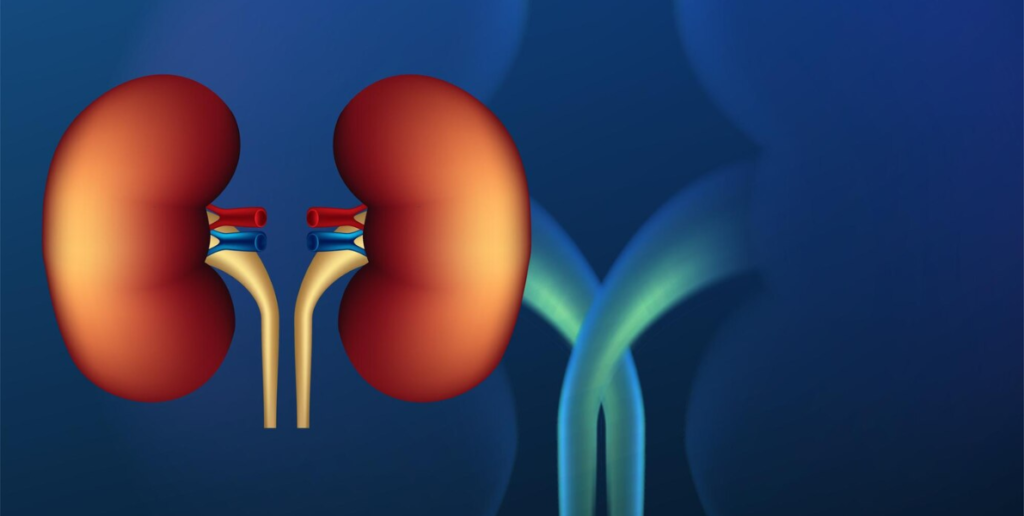
The kidneys filter waste from the blood, but elevated glucose levels can overwork and damage them. Over time, this may lead to kidney failure, necessitating dialysis or a kidney transplant.
6. Vision Problems (Diabetic Retinopathy)
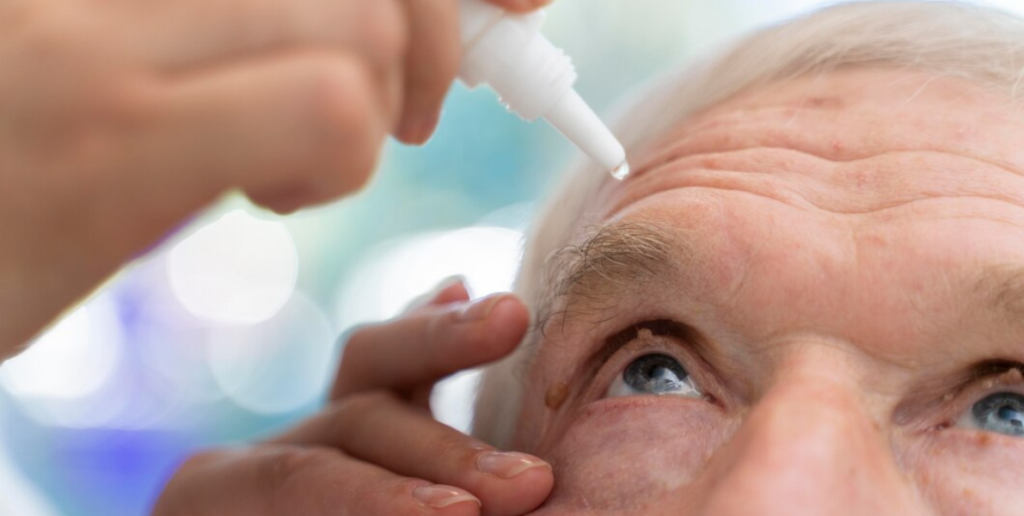
Diabetes can harm the blood vessels in the eyes, leading to diabetic retinopathy, which, if untreated, may cause vision impairment or blindness.
7. Slow Wound Healing
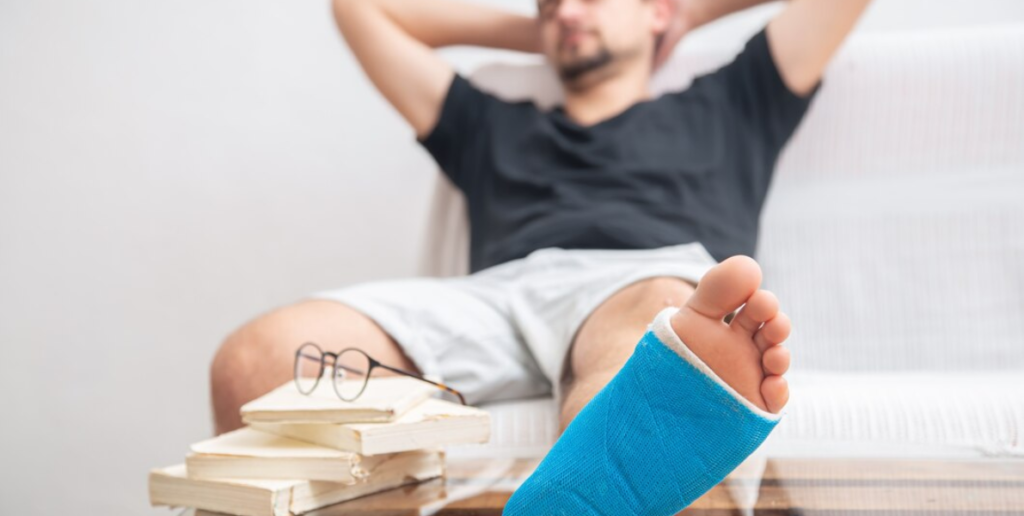

Diabetes impairs circulation and immune function, slowing the healing process. Minor cuts and wounds may take longer to recover and are more prone to infection.
Strategies for Improvement and Management
Although diabetes is a lifelong condition, proper management can greatly improve health outcomes. Below are some key ways to control diabetes and reduce associated risks.
1. Follow a Balanced Diet
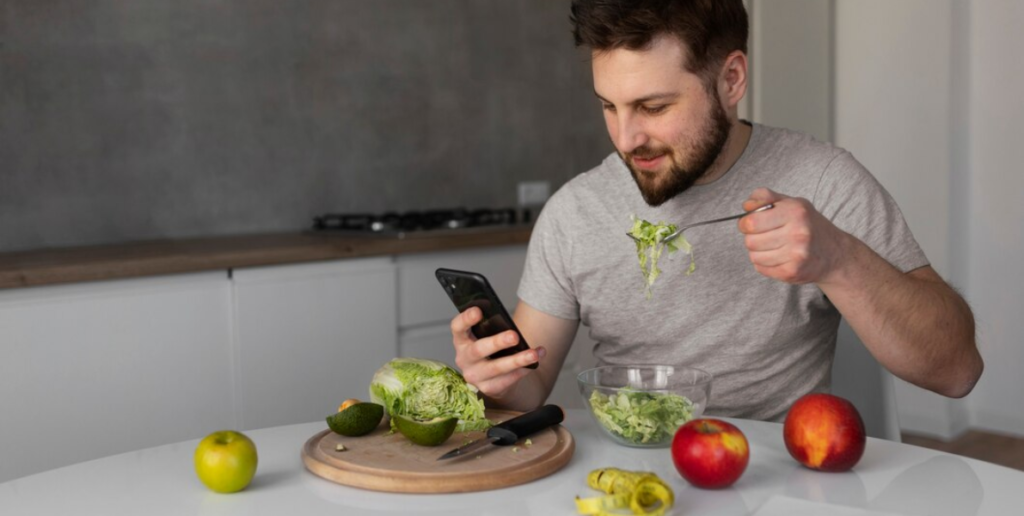

A nutritious diet plays a vital role in managing diabetes. Key dietary recommendations include:
- Eat fibre-rich foods: whole grains, vegetables, fruits, and legumes help regulate blood sugar levels.
- Opt for complex carbohydrates: choose brown rice, whole wheat, and oats instead of refined grains.
- Reduce sugar intake: minimise consumption of sugary drinks, desserts, and processed foods.
- Incorporate lean proteins: Fish, poultry, tofu, and legumes support muscle health without spiking blood sugar.
- Consume healthy fats: avocados, nuts, and olive oil provide beneficial fats that lower heart disease risks.
2. Engage in Regular Exercise
Physical activity enhances insulin sensitivity and aids in glucose regulation. Consider the following:
- Aerobic exercises: Activities like walking, jogging, cycling, and swimming benefit heart health.
- Strength training: Resistance exercises and weightlifting help maintain muscle mass.
- Flexibility and balance exercises: yoga and stretching improve mobility and prevent injuries.
- Stay consistent: aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate exercise per week.
3. Monitor Blood Sugar Levels
Frequent blood sugar monitoring helps prevent spikes or drops. Keeping a glucose log and consulting a healthcare provider can aid in tailoring treatment plans effectively.
4. Proper Medication and Insulin Use
For those prescribed medication or insulin, adherence is essential. Skipping doses or taking incorrect amounts can lead to severe complications. Consult a doctor to determine the best treatment plan.
5. Stay Hydrated
Adequate hydration supports kidney function and helps regulate blood sugar levels. Water is the best option, while sugary beverages should be avoided.
6. Manage Stress Effectively
Stress can elevate blood sugar levels, making diabetes harder to control. Stress-reducing activities include
- Practicing meditation and mindfulness
- Engaging in breathing exercises
- Pursuing hobbies
- Spending time outdoors
7. Get Sufficient Sleep
Lack of sleep disrupts insulin function, leading to poor blood sugar control. Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night.
8. Schedule Regular Health Checks
Routine medical checkups help track diabetes progression and prevent complications. Essential tests include:
- HbA1c tests: Measure average blood sugar levels over a few months.
- Blood pressure and cholesterol screenings
- Kidney function assessments
- Eye and foot examinations
9. Quit Smoking and Limit Alcohol Consumption
In diabetic health issue Smoking raises the risk of heart disease, stroke, and nerve damage, making it crucial to quit. Additionally, excessive alcohol can cause blood sugar fluctuations, so moderation is essential.
10. Prioritise Foot Care
Since diabetes affects circulation and nerve function, proper foot care is necessary:
- Inspect feet daily for any cuts, sores, or infections.
- Wash and moisturise feet regularly.
- Wear comfortable, well-fitting shoes.
- Seek medical attention for slow-healing wounds.
Conclusion
Managing diabetic health issues, but with the right lifestyle modifications and proactive strategies, individuals can maintain a healthy and fulfilling life. Prioritising diet, exercise, stress management, and routine check-ups helps minimise complications and enhances overall well-being. Early intervention, education, and self-care are essential in leading a healthier future. Take charge of your diabetic health issues today and make informed decisions for a better tomorrow!









No Comments
Leave Comment